Flexible magnets, Permanent magnets
, Magnetic lifter, Magnetic filter, Magnetic label holder, Magnetic badge holder
 Your magnetic products sources
Your magnetic products sources
MACMILL Magnets Co.,Ltd.
Macmill Magnet
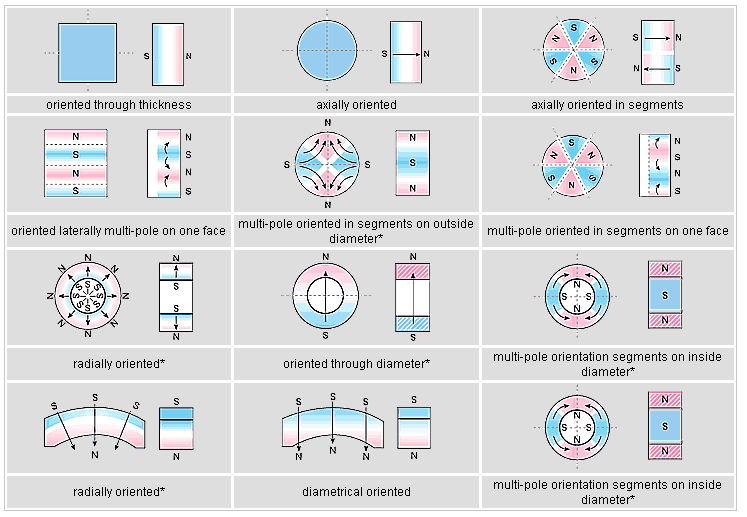
Anisotropic Magnet:
A magnet having a preferred direction of magnetic orientation, so that the magnetic characteristics are optimum in that direction.
♦
Coercive force, Hc:
The demagnetizing force, measured in Oersted, necessary to reduce observed induction, B to zero after the magnet has previously been brought to saturation.
♦
Curie temperature:
The temperature at which the parallel alignment of elementary magnetic moments completely disappears, and the materials is no longer able to hold magnetization.
♦
Flux:
The condition existing in a medium subjected to a magnetizing force. This quantity is characterized by the fact that an electromotive force is induced in a conductor surrounding the flux at any time the flux changes in magnitude. The unit of flux in the GCS system is Maxwell. One Maxwell equals one volt*seconds.
♦Gauss, Gs:
A unit of magnetic flux density in the GCS system; the lines of magnetic flux peer square inch.1 Gauss equals 0.0001 Tesla in the SI system.
♦Induction, Br:
The magnetic flux per unit area of a section normal to the direction of flux. The unit of induction is Gauss in the GCS system.
♦
Intrinsic Coercive Force, iHc:
An intrinsic ability of a material to resist demagnetization. Its value is measured in Oersted and corresponds to zero intrinsic induction in the material after saturation. Permanent magnets with high intrinsic coercive force are referred as "Hard" permanent magnets ,which usually associated with high temperature stability.
♦
Maximum Energy Product, (BH) max:
There is a point at the hysteresis Loop at which the product of magnetizing force Hand induction B reaches a maximum. The maximum value is called the Maximum Energy Product. At this point, the volume of magnet material required to project a given energy into its surrounding is a minimum. This parameter is generally used to describe how "strong" this permanent magnet material is. Its unit is Gauss Oersted. One MGOe means 1,000,000 Gauss Oersted.
♦Oersted, Oe:
A unit of magnetizing force in GCS system.1 Oersted equals 79.58 A/m in SI system.
♦Irreversible Loss:
Defined as the partial demagnetization of a magnet caused by external fields or other factors. These losses are only recoverable by demagnetization. Magnets can be stabilized to prevent the variation of performance caused by irreversible
♦Polymer_ Bonding:
Magnet powders are mixed with a polymer carrier matrix, such as epoxy. The magnets are formed in a certain shape, when the carrier is solidified.
♦Residual Induction, Br:
A value of induction at the point at Hysteresis Loop, at which Hysteres is loop crosses the B axis at zero magnetizing force. The Br represents the maximum magnetic flux density output of this material without an external magnetic field.
♦Saturation:
A condition under which induction of a ferromagnetic material has reach its maximum value with the increase of applied magnetizing force. All elementary magnetic moments have become oriented in one direction at the saturation status.
♦Sintering;:
The bonding of powder compacts by the application of heat to enable one or more of several mechanisms of atom movement into the particle contact interfaces to occur; the mechanisms are: viscous flow, liquid phase solution-precipitation, surface diffusion, bulk diffusion, and evaporation-condensation. Densification is a usual result of sintering.
♦Stability :
An ability to resist to demagnetizing influence expected to be encountered in operation. These demagnetizing influences can be caused by high or low temperatures or by extremely magnetic fields.
♦Demagnetization Curve:
The second quadrant of the hysteresis loop, generally describing the behavior of magnetic characteristics in actual use, Also known as the B-H curve.North Pole: That pole of a magnet which, when freely suspended, would point to the north magnetic pole of the earth. The definition of polarity can be a confusing issue,
and it is often best to clarify by using "north seeking pole" instead of "north pole" in specifications
♦Magnetized direction: